Pheidole
| Pheidole | |
|---|---|
| |
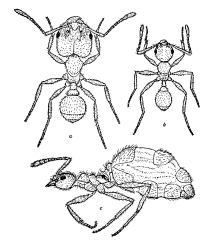
| Pheidole dentata | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | Myrmicinae |
| Tribe: | Attini |
| Genus: | Pheidole Westwood, 1839 |
| Species | |
|
Many, see text | |
| Diversity[1][2] | |
| 1,301 species | |

Pheidole (Ancient Greek pronunciation: [pʰeː.dɔː.le]) is a genus of ants that belongs to the ant subfamily Myrmicinae. The genus is widespread and ecologically dominant. Many species in the genus first evolved in the Americas, while some, such as Pheidole indica and Pheidole megacephala, originated from East Asia and Africa, respectively.[3] These species eventually began spreading across the globe. Pheidole megacephala is considered a particularly problematic invasive species.[3]

Colony structure
[edit]Most species of Pheidole are dimorphic, which means that colonies contain two castes of workers, the "minor" workers, and the "major" workers, or "soldiers". The latter generally have much larger heads and mandibles in comparison to their usually fairly modest body size. [4] This caste is also notable due to the presence of wings, found in the queen ants as well as in the males.[5]
A colony may contain one or several queens, and also in larger colonies of Pheidole morrisi, alates - virgin winged females and males - were found.[6] Queens appear to allocate reproductive resources between queens and worker ants, and tend to favour one or the other in terms of allocation.[7]
-
major and minor workers of P. xerophila
Morphology
[edit]Pheidole are ants which belong to the order Hymenoptera that includes organisms such as wasps, bees, ants and sawflies. Their body is divided into four main sections which include the head, mesosoma, waist and gaster that help differentiate them from other organisms in the order[8].
Head
[edit]The head of Pheidole is the main distinctive feature between other species and within the physical castes present in colonies[9]. In general, the head is composed of antennae, mandibles, clypeus, and compound eyes[8]. The antennae serve as the feelers of the head [8]. In ants, each antennae is elbowed meaning a scape is followed by long basal segment which articulates with the head [8]. In Pheidole, the antennae are 12-segmented with a distinct 3-segmented club which helps differentiate the genus[10]. Furthermore, the head allows us to tell apart the two physical worker castes[9]. The major or soldier workers display a much bigger head than the minor workers which can be used for defense of the colony[9]. The head of Pheidole contains six structures that are found in most species[11]. It contains muscle tissue, nervous system, the esophagus-pharynx, the propharyngeal glands, the postpharyngeal glands and the mandibular glands[11]. The pharynx is located anteriorly at the base of the mouthparts and is connected to esophagus posteriorly[11]. The ventral cord is paired ventrally with the esophagus and connects anteriorly to the brain[11]. The ventral cord is also connected to the optic and antennal nerves via nervous tissue[11]. The propharyngeal are smaller than the postpharyngeal glands and are located posterior to the pharynx while the postpharyngeal glands are located ventral to the esophagus[11]. Finally, the mandibular glands are located posterior to the clypeus and are site of attachments for muscles[11].
Mesosoma
[edit]This section contains the prothorax, mesothorax, metanotum and propodeum[8]. The pronotum is the upper portion of prothorax and specifically in Pheidole makes up almost all of the prothorax when viewed from above or laterally[8]. As the name suggests, the mesothorax is the middle segment of the thorax and includes the mesonotum or the top portion and the mesopleuron which is the side portion[8]. This is followed by the metanotum which is the top portion of the farthest back segment of the thorax[8]. This is usually located in between the mesothorax and the propodeum[8]. Lastly, the propodeum is the rear segment of the thorax[8]. A distinctive feature regarding Pheidole is the depression of propodeum below the promesonotum, the combined pronotum and mesonotum area[10]. This area uniquely also has teeth or spines[10].
Waist and Gaster
[edit]The waist serves the function of connecting the middle portion of the body to the hindmost portion known as gaster[8]. Most members of the subfamily Myrmicinae have a 2-segmented waist which is composed of petiole followed by post petiole[8]. The gaster specifically holds functions related to alarm and defense which will be explored in later sections.
Behaviour and Ecology
[edit]The world of ants is highly social. With various physical castes present in a single colony, it is imperative to develop biological systems that regulates and directs various functions to ensure survival of the colony. The following section provides information regarding how ants, Pheidole in particular, organize these functions.
Methods of Communication, Defense and Learning
[edit]The success hyper diverse genus of Pheidole is largely attributed to their ability to communicate when under threat. Many species specifically are exposed to intense interspecific competition with fire ants, Solenopsis[9]. Initially, the aggressors (fire ants) are contacted with minor workers foraging for food[9]. Upon this, the Pheidole minor workers swiftly run back and forth to the nest while ensuring contact of their gaster with the ground[9]. This results in the deposition of pheromones into the soil which serve as a guide for both minor and major workers to follow[9]. Furthermore, in an ecological setting where the interspecific competition is heightened, many colonies will upregulate the number of soldier pupae and adults[9]. The poison gland within the abdomen is responsible for the secretion of this hormone[12]. This process is similarly followed during cultivation of food. Environmental cues also determines the role physical castes play in the colony[9]. If larger and more abundant resources are present, soldier workers will be tasked with foraging and overtime their ratio in the colony will be decreased and replaced with minor workers[9]. This demonstrates learning within the colony. The main factor that differs communication for food from communication against a threat is the presence of odor[12]. If a minor worker had contacted a fire ant and was returned to the nest immediately, it was met with aggression and hostility[12].
Development of Nests and Colonies
[edit]Seasonal cues such as increase in sunlight and elevated temperatures cause the development of reproductive queens and males in mature colonies[9]. Due to the energy expenditure of queens and soldiers being equal, the production of soldiers is halted while queens and males are created[9]. After reproduction, the queen tears off its wings which signals the establishment of a colony[9]. Most premature colonies choose to develop small minor workers initially to secure food supply[9]. However, as the colony grows, the minor workers gradually become larger as well[9]. Similarly, after minor workers have been produced, the queen undergoes similar process for soldiers that initially start off small and gradually become a larger size found that is found in mature colonies[9].
Distribution and Diversity
[edit]Pheidole are a highly diverse genus that can be found in many regions, generally preferring warmer climates such as tropical rainforests where the largest diversity of Pheidole are typically found. Although they prefer these warmer climates, Pheidole can be also found in a very wide range of climates and ecosystems from rainforests, to deserts, to grasslands. In these ecosystems, Pheidole are found most commonly in the soil and litters. The diet of this genus is typically generalized, with nuts, leaves, nectar being common food choices but many species typically lean towards predation to supplement their diet.[13][8]
Major workers
[edit]The distinctive major workers have earned the genus Pheidole the nickname of "big-headed ants". The major workers of a Pheidole colony, while they may look fierce, are often quite shy and are often the first to flee on any hint of danger. Many Pheidole species are the prey of parasitoid phorid flies that lay their eggs on the major workers; the fly larvae grow mainly in the head capsules of the victims, eventually decapitating them, and probably would starve in the bodies of minor workers.[citation needed]
In most cases, the major workers are employed within the nest to break up large food items, or outside to carry large items, such as seeds; many Pheidole species are ecologically important seed consumers ("harvesters").[citation needed]
- Minor and major workers of P. purpurea
-
Minor worker
-
Minor worker, top
-
Major worker
-
Major worker, top
Minor workers
[edit]Minor workers typically get bigger over time, despite initially starting out as small "nanitic" individuals when the colony is first created.[9]
Economic Impacts and Relationships with Humans
[edit]Members of Pheidole hold an important role in the tropical agroecosystems that they are abundant in. Due to many Pheidole species being strong predators with aggressive tendencies, their nests are associated with a high presence of arthropod carcasses from their hunts. As a result, the soils that surround their nests show strongly improved nutrient density that improves their ecosystems.[14][15]
Although the aggressive predation from Pheidole may benefit the ecosystems they originate from, many members of this genus are considered highly invasive species with Pheidole megacephala named as one of the 100 worst invasive species in the world.[16] The invasive capabilities of Pheidole megacephala are tied to the aggressiveness of genus Pheidole, as within their native environments, they reside in an extremely diverse ecosystem with many other species compete against, many of which are also very aggressive. Finding themselves in environments with less diversity and decreased aggression from other species, lead to successful raids of local ant colonies.[17]
Species list
[edit]The genus contains over 1,000 species.[18] They include:
- Pheidole acutidens
- Pheidole argentina
- Pheidole barreleti
- Pheidole bicarinata
- Pheidole bigote
- Pheidole branstetteri
- Pheidole braueri
- Pheidole bula
- Pheidole carinote
- Pheidole cervicornis
- Pheidole ceylonica
- Pheidole clavata
- Pheidole debilis
- Pheidole decepticon
- Pheidole dentata
- Pheidole diffidens
- Pheidole dodo
- Pheidole elecebra
- Pheidole elongicephala
- Pheidole eowilsoni
- Pheidole epiphyta
- Pheidole fervens
- Pheidole fossimandibula
- Pheidole gracilipes
- Pheidole gymnoceras
- Pheidole harlequina
- Pheidole harrisonfordi
- Pheidole horni
- Pheidole inquilina
- Pheidole janzeni
- Pheidole jonas
- Pheidole karolmorae
- Pheidole karolsetosa
- Pheidole komori
- Pheidole laevithorax
- Pheidole lagunculinoda
- Pheidole lanuginosa
- Pheidole latinoda
- Pheidole leoncortesi
- Pheidole loki
- Pheidole malinsii
- Pheidole megacephala
- Pheidole megatron
- Pheidole microgyna
- Pheidole neokohli
- Pheidole nietneri
- Pheidole noda
- Pheidole obtusospinosa
- Pheidole ochracea
- Pheidole oculata
- Pheidole pallidula
- Pheidole pararugiceps
- Pheidole parasitica
- Pheidole parva
- Pheidole pegasus
- Pheidole phanigaster
- Pheidole picobarva
- Pheidole pronotalis
- Pheidole psilogaster
- Pheidole purpurea
- Pheidole ragnax
- Pheidole rhea
- Pheidole rhinomontana
- Pheidole rugithorax
- Pheidole rugosa
- Pheidole sebofila
- Pheidole simplispinosa
- Pheidole spathifera
- Pheidole sulcaticeps
- Pheidole symbiotica
- Pheidole templaria
- Pheidole teneriffana
- Pheidole uncagena
- Pheidole vieti
- Pheidole vulcan
- Pheidole xerophila
References
[edit]- ^ E. O. Wilson (2003). Pheidole in the New World: A Dominant, Hyperdiverse Ant Genus. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-00293-8.
- ^ Shattuck, Steven O. "Pheidole". AntWiki. antwiki.org. Retrieved 14 October 2024.
- ^ a b Sarnat, Eli M.; Fischer, Georg; Guénard, Benoit; Economo, Evan P. (9 December 2015). "Introduced Pheidole of the world: taxonomy, biology and distribution". ZooKeys (543): 1–109. Bibcode:2015ZooK..543....1S. doi:10.3897/zookeys.543.6050. ISSN 1313-2989. PMC 4714327. PMID 26798286.
- ^ Muscedere, Mario L.; Traniello, James F. A. (February 17, 2012). "Division of Labor in the Hyperdiverse Ant Genus Pheidole Is Associated with Distinct Subcaste- and Age-Related Patterns of Worker Brain Organization". PLOS ONE. 7 (2). PLOS: e31618. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...731618M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031618. PMC 3281964. PMID 22363686.
- ^ Rajakumar, Rajendhran; Koch, Sophie; Couture, Mélanie; Favé, Marie-Julie; Lillico-Ouachour, Angelica; Chen, Travis; De Blasis, Giovanna; Rajakumar, Arjuna; Ouellette, Dominic; Abouheif, Ehab (10 October 2018). "Social regulation of a rudimentary organ generates complex worker-caste systems in ants". Nature. 562 (7728): 574–577. Bibcode:2018Natur.562..574R. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0613-1. ISSN 1476-4687.
- ^ Murdock, T. C.; Tschinkel, W. R. (2015-08-01). "The life history and seasonal cycle of the ant, Pheidole morrisi Forel, as revealed by wax casting". Insectes Sociaux. 62 (3): 265–280. doi:10.1007/s00040-015-0403-9. ISSN 1420-9098.
- ^ Fournier, D.; Aron, S.; Keller, L. (2004). "Significant reproductive skew in the facultatively polygynous ant Pheidole pallidula". Molecular Ecology. 13 (1): 203–210. Bibcode:2004MolEc..13..203F. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.02036.x. ISSN 1365-294X.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Wilson, Edward O. (2003). Pheidole in the new world : a dominant, hyperdiverse ant genus. Internet Archive. Cambridge, Mass. : Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-00293-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Lillico-Ouachour, Angelica; Abouheif, Ehab (2017-02-01). "Regulation, development, and evolution of caste ratios in the hyperdiverse ant genus Pheidole". Current Opinion in Insect Science. 19: 43–51. Bibcode:2017COIS...19...43L. doi:10.1016/j.cois.2016.11.003. ISSN 2214-5745. PMID 28521942.
- ^ a b c Fisher, Brian L.; Cover, Stefan P. (2007-11-02). Ants of North America. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-93455-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g Lillico-Ouachour, Angelica; Metscher, Brian; Kaji, Tominari; Abouheif, Ehab (2018-05). "Internal head morphology of minor workers and soldiers in the hyperdiverse ant genus Pheidole". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 96 (5): 383–392. doi:10.1139/cjz-2017-0209. ISSN 0008-4301.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b c Wilson, Edward O. (1976). "The organization of colony defense in the ant Pheidole dentata mayr (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 1 (1): 63–81. doi:10.1007/bf00299953. ISSN 0340-5443.
- ^ Casadei Ferreira, Alexandre (2021), "Pheidole", in Starr, Christopher K. (ed.), Encyclopedia of Social Insects, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 728–731, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-28102-1_172, ISBN 978-3-030-28102-1, retrieved 2025-03-26
- ^ Shukla, R. K.; Singh, H.; Rastogi, N.; Agarwal, V. M. (2013-09-01). "Impact of abundant Pheidole ant species on soil nutrients in relation to the food biology of the species". Applied Soil Ecology. 71: 15–23. Bibcode:2013AppSE..71...15S. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.05.002. ISSN 0929-1393.
- ^ Wang, Shaojun; Li, Jihang; Zhang, Zhe; Chen, Minkun; Li, Shaohui; Cao, Run (2019-01-01). "Feeding-strategy effect of Pheidole ants on microbial carbon and physicochemical properties in tropical forest soils". Applied Soil Ecology. 133: 177–185. Bibcode:2019AppSE.133..177W. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.10.006. ISSN 0929-1393.
- ^ Sarnat, Eli M.; Fischer, Georg; Guénard, Benoit; Economo, Evan P. (2015). "Introduced Pheidole of the world: taxonomy, biology and distribution". ZooKeys (543): 1–109. Bibcode:2015ZooK..543....1S. doi:10.3897/zookeys.543.6050. ISSN 1313-2989. PMC 4714327. PMID 26798286.
- ^ Dejean, Alain; Moreau, Corrie S.; Kenne, Martin; Leponce, Maurice (2008-08-01). "The raiding success of Pheidole megacephala on other ants in both its native and introduced ranges". Comptes Rendus Biologies. 331 (8): 631–635. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2008.05.004. ISSN 1631-0691. PMID 18606393.
- ^ Bolton, B. (2014). "Pheidole". AntCat. Retrieved 17 January 2015.
External links
[edit] The dictionary definition of pheidole at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of pheidole at Wiktionary Media related to Pheidole at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Pheidole at Wikimedia Commons- Myrmecos.net images of live Pheidole
- gallery of Pheidole specimen images, on Antweb.org





